

#!/usr/bin/python
# Bitbanging code to use Parallax serial RFID reader
# Terry Sturtevant, May 9, 2017
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
from datetime import datetime
import time
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
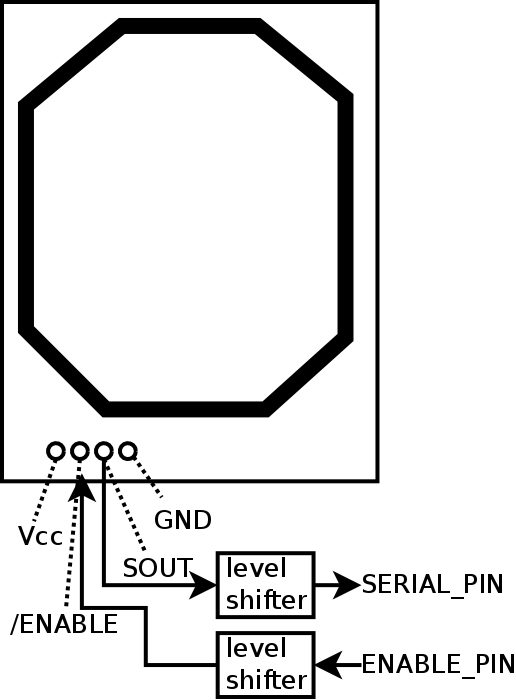
ENABLE_PIN=5
#This could presumeably be modified for other serial devices
PORT_RATE=2400
BYTESIZE=8
PARITY="N"
STOP_BITS=1
END_LINE='\n'
# any GPIO pin can be used
SERIAL_PIN=27
START_LEVEL=False
STOP_LEVEL=True
HALF_BIT_TIME=1/float((2*PORT_RATE))
THREE_HALF_BIT_TIME=3*HALF_BIT_TIME
ONE_BIT_TIME=2*HALF_BIT_TIME
HALF_BIT_TIME_US=int(HALF_BIT_TIME*1000000)
THREE_HALF_BIT_TIME_US=int(1000000*THREE_HALF_BIT_TIME)
ONE_BIT_TIME_US=int(1000000*ONE_BIT_TIME)
#in seconds
ALLOWABLE_DEAD_TIME=1
CHAR_TIME_US=(BYTESIZE*2+STOP_BITS)*HALF_BIT_TIME_US
message=[]
chartimes=[]
#In order to be fast enough in Python, this routine just generates an array
# of transition times on the serial pin (in microseconds)
# At the beginning of each new character, the time is reset to zero
# (Number of transitions for a character must be odd)
##
def timeChar():
timestart=0
times=[]
# wait for start bit
input_value=GPIO.input(SERIAL_PIN)
while input_value != START_LEVEL:
input_value=GPIO.input(SERIAL_PIN)
# get data transition time of start bit
dt=datetime.now()
nowus=dt.microsecond
times.append(nowus)
timestart=nowus
#calculate time for the entire character
timeend=timestart+CHAR_TIME_US
# get data transition time of other bits
# stop when the time for the entire character has passed
while nowus<timeend:
oldLevel=input_value
input_value=GPIO.input(SERIAL_PIN)
while input_value == oldLevel:
input_value=GPIO.input(SERIAL_PIN)
dt=datetime.now()
nowus=dt.microsecond
times.append(nowus)
times.append(times[0])
# wait for stop bit
input_value=GPIO.input(SERIAL_PIN)
while input_value != STOP_LEVEL:
input_value=GPIO.input(SERIAL_PIN)
#now make times relative to the start of the character
#so the start bit is at 0, by definition
temptime=times[0]
for i in range(len(times)):
times[i]=times[i]-temptime
return times
# given an array of transition times, and knowing the time for a bit,
# and that the character starts with a START bit, the complete
# bit string can be generated
# The data comes in LSB first, so it gets reversed at the end
##
def convertChar(thesetimes):
bytestr=''
curtime=0
curLevel='1'
altLevel='0'
curBit=0
if thesetimes[1]<CHAR_TIME_US:
for i in range(len(times)):
while thesetimes[i]>curtime+THREE_HALF_BIT_TIME_US:
bytestr+=curLevel
curtime+=ONE_BIT_TIME_US
curBit+=1
tempLevel=curLevel
curLevel=altLevel
altLevel=tempLevel
return bytestr[::-1]
####################MAIN##################
#beginning of main code
#The reader has an ENABLE pin, which must be LOW to read
GPIO.setup(ENABLE_PIN,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(SERIAL_PIN,GPIO.IN)
#This just makes a flash of the LED
GPIO.output(ENABLE_PIN,GPIO.HIGH)
time.sleep(0.5)
GPIO.output(ENABLE_PIN,GPIO.LOW)
try:
charSpace=0
msgIndex=1
startTime=datetime.now()
msgTime=startTime-startTime
msgStarted=False
msgDone=False
#A message will be assumed to be complete if there
# hasn't been a transition in ALLOWABLE_DEAD_TIME (seconds)
#Processing of transisiton times isn't done until AFTER
# the message is complete to allow a higher baud rate
while not msgDone:
#wait for activity
input_value=GPIO.input(SERIAL_PIN)
if input_value == STOP_LEVEL:
thisTime=datetime.now()
if not msgStarted:
startTime=thisTime
msgTime=thisTime-startTime
if msgTime.seconds>ALLOWABLE_DEAD_TIME:
msgDone=True
else:
# get a character
chartimes=timeChar()
startTime=datetime.now()
msgStarted=True
message.append(chartimes)
msgIndex+=1
#message is done, so disable reader
GPIO.output(ENABLE_PIN,GPIO.HIGH)
#now process transition times
charstr=''
for i in range(msgIndex-1):
times=message[i]
value=convertChar(times)
ascval= int(value,2)
charstr+= chr(ascval)
times=[]
print charstr
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
GPIO.cleanup()



Wilfrid Laurier University
© 2019 Wilfrid Laurier University