PC/CP320 Physical Computing
Raspberry Pi Python PWM
Objectives
- To become familiar with Raspberry Pi GPIO pins and
BOARD and BCM numbering schemes
- To learn nano editor commands
- To learn about Pulse Width Modulation channels on the
Raspberry Pi
Preparation
Equipment
- Raspberry Pi
- TTL-serial to USB adapter
- 2 LEDs and 1k resistors. (Depending on brightness, you may
need a smaller resistor.)
- breadboard
Procedure

|
The Rapsberry Pi GPIO pins can easily be damaged with
improper handling.
|
-
Testing the Serial adapter driver
installation
Connect the TTL-serial cable
via the USB cable to the computer.
Open the Device Manager and check to see what COM port the
adapter appeared on.
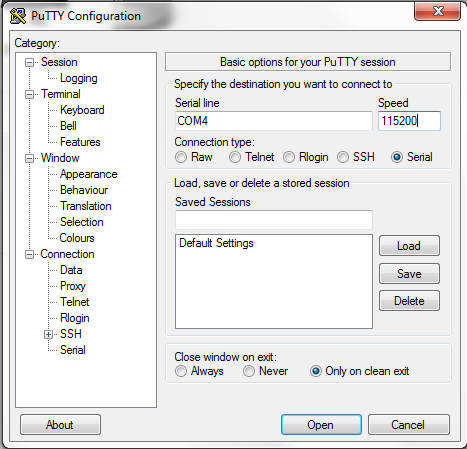
- Open putty, and set it for
serial on the COM port just noted and set the
baud rate to 115200.
-
Any time you connect anything to the
GPIO pins, make
sure you know the correct orientation!!!
Connect the TTL-serial cable to the Raspberry Pi as
follows:
- Don't connect the red
wire.
- Connect the black wire to GROUND.
- Connect the white wire to TxD.
Use a white wire for the connection!
- Connect the green wire to RxD.
Use a green wire for the connection!
- Plug in the Pi, and you should see the boot process in the
serial console and get a login prompt as expected.
Show this to the lab
instructor.
-
Here are some common commands for linux. Note that the cursor up
and down keys take you through a history of previously used commands.
| Common linux commands
|
| Command
|
Description
|
Example
|
|
ls
|
list files in directory
|
ls
*.py
|
|
cp
|
copy a file
|
cp
test.py newtest.py
|
|
mv
|
move (or rename) a file
|
mv
oldtest.py newtest.py
|
|
sudo
|
execute program as superuser
|
sudo
python3 test.py
|
|
mount
|
mount external (flash) drive
|
mount
/mnt/usb
|
|
umount
|
unmount external (flash) drive
|
umount
/mnt/usb
|
|
shutdown
|
shutdown computer properly
|
sudo shutdown
-h now
|
Here are some common commands for nano.
| Common nano commands
|
| Command
|
Description
|
|
CTRL-K
|
cut line(s)
|
|
CTRL-U
|
uncut line(s) (i.e. paste)
|
|
CTRL-X
|
save and quit
|
|
CTRL-O
|
save without quitting
|
-
Using Pulse Width Modulation on GPIO18
Broadcom pin GPIO18 has the ability to produce asquare wave
output using Pulse Width
Modulation or PWM. Once started, a square wave
will be produced without the program having to toggle the pin
explicitly. To set it up, after the pin is set to output
p = GPIO.PWM(12, 60)
will set up the pin for a 60Hz waveform.
p.start(50)
will turn it ON with a 50% duty cycle and
p.stop()
will turn it OFF.
p.ChangeDutyCycle(20)
will change the duty cycle to 20% without stopping it
and
p.ChangeFrequency(100)
will change the frequency to 100Hz without stopping.
Download pwm_test_2018.py
-
Now wire up the LED and resistor
on the breadboard, and connect them
to the pin, and
run the program to
see how changing
the duty cycle changes the brightness.
- Change the frequency to see how low it can go before you see
the LED flickering.
- Change the duty cycles to see how small a difference in
brightness you can detect.
- Remove (or comment out) the command to stop the pwm at the
end of the
program. Run the program and see what happens when the program
stops. (You may need to remove the cleanup line as well.)
-
As before, modify the program to use the same pin GPIO18
but using the Broadcom
numbering scheme.
Demonstrate the output using the scope and LED
and the effect of changing the duty cycle
to the lab
instructor.
-
Using the other Pulse Width Modulation channel.
Look up the location of PWM1.
-
Copy the test program to a new one and change it to work with
this new pin.
Now connect an LED and resistor to this pin, and
run the program to
show that it works correctly.
- Create a program which combines the two, so that the duty
cycles are opposites for the two LEDS. (So if one is 10%, the
other will be 90%, and so on.)
- Change the duty cycles to see how small a difference in
brightness you can detect.
-
Modify the program so that the duty cycle increases from 0 to
100% over 10 seconds for one, with the other having the
opposite duty cycle, as in the question above.
Demonstrate the output
to the lab
instructor.
-
Proper shutdown
Shut down the pi using
sudo shutdown -h now
When shutdown is complete, you can disconnect power and put
everything away.
Wilfrid Laurier University
© 2019 Wilfrid Laurier University